Let’s Connect & Accelerate Your Organic Growth
- Your data is properly secured encrypted by SSL
As your website grows, it’s easy to believe that adding more pages will automatically bring more traffic. Many teams do exactly that. But over time, the results can be disappointing.
Instead of helping, some pages start competing with each other in Google search results. When this happens, search engines get confused about which page to rank. This issue is called content cannibalization, and it can slowly hurt your rankings, traffic, and even conversions often without any clear warning.
In this blog, we’ll look at what content cannibalization really means, why it usually happens on growing websites, how to spot it early, and how to fix it at scale without risking your existing rankings.
Why Content Cannibalization Is a Silent SEO Problem
Content cannibalization often goes unnoticed because the symptoms aren’t obvious. You may notice:
- Fluctuating rankings for key pages
- Lower click-through rates
- Confusion over which page should rank
Even if all your content is high quality, Google struggles to decide which page to show. That means none of your pages get their full potential.
What Content Cannibalization Really Looks Like
It’s easy to confuse cannibalization with normal competition. But here are common scenarios:
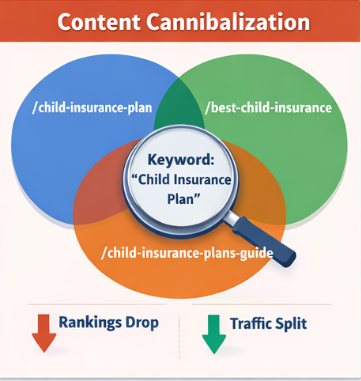
When Multiple Pages Target the Same Keyword
For example, imagine your site has:
- /child-insurance-plan
- /best-child-insurance
- /child-insurance-plans-guide
All three target the keyword “child insurance plan.” Google sees them as competing pages. Instead of ranking one page high, it spreads traffic between all three — or sometimes, none rank consistently.
When Google Keeps Switching Rankings
You might notice Page A ranks for a keyword one week, and Page B the next. This happens when your content overlaps too much, confusing search engines.
Why More Content Sometimes Hurts Rankings
It’s tempting to think “more content = more traffic,” but that’s not always true. Cannibalization occurs when:
- Pages cover the same topic repeatedly
- New pages are created without checking existing content
- Blog posts start competing with service or product pages
The result is a scattered SEO signal. Instead of one strong page, you have multiple weaker ones.
How Content Cannibalization Impacts Your Website
The effects can be serious:
Fluctuating Rankings
Google doesn’t know which page to prioritize, so rankings jump around.
Wasted Clicks
Users see different pages for the same topic. Confusion reduces trust and engagement.
Lost Authority
Backlinks and internal links are split across multiple pages instead of strengthening a single authority page.
Crawl Budget Issues
Google spends time crawling duplicate or similar content instead of important pages, slowing overall indexing.
How to Spot Content Cannibalization
Finding cannibalization isn’t just about matching keywords — you need to understand intent and performance.
Using Google Search Console
- Go to Performance → Search results
- Look for a keyword with multiple pages ranking
- Check impressions and clicks
If more than one page gets impressions for the same query, that’s a warning sign.

Using a Keyword-to-URL Sheet
Create a simple sheet with:
- URL
- Target keyword
- Secondary keywords
- Page type (blog, service, category)
- Clicks & impressions
If multiple URLs share the same keyword and intent, you likely have cannibalization.
Manual SERP Checks
Search your target keywords and analyze top results:
- Which page type dominates the SERP?
- Are your pages aligning with user intent?
If your pages don’t match the dominant intent, they may compete unnecessarily.
Fixing Content Cannibalization Without Breaking Your Rankings
Once you identify cannibalization, fixing it requires careful planning, especially at scale.
Choose a Primary Page
Decide which page should be the main authority for each keyword cluster. Consider:
- Existing traffic and ranking
- Conversions or leads generated
- Alignment with business goals
This page becomes the main page. All others should support it.
Merge Similar Content
When multiple pages serve the same purpose:
- Combine the best sections into the primary page
- Add updated examples, visuals, and headings
- Redirect the secondary pages to the primary page using 301 redirects
This consolidates authority and signals to Google which page to prioritize.

Differentiate Pages by Intent
Sometimes both pages are valid but serve different intent:
- “What is Term Insurance?” (informational)
- “Buy Term Insurance Online” (transactional)
To fix:
- Rewrite headings and content to match intent
- Adjust internal links accordingly
- Ensure Google understands the difference
Convert Competing Blogs into Support Pages
If blogs are cannibalizing service pages:
- Keep them educational
- Link to the primary service page
- Avoid duplicate keywords in blog titles
This lets the service page dominate commercial searches.
How to Strengthen Internal Linking
Internal linking guides Google to the right page.
- Link supporting pages to the primary page
- Use natural anchor text
- Avoid repeating the exact anchor everywhere
A clear internal link strategy reinforces your authority page and prevents future cannibalization.
How to Handle Old and Thin Content
Old or low-value pages often cause cannibalization. Options:
- Merge into existing authority pages
- Redirect to relevant pages
- Noindex pages with little SEO value
- Delete only if the page truly serves no purpose
Every page should have a clear role in your website strategy.
Preventing Content Cannibalization as Your Site Grows
The best way to avoid this problem is planning before publishing.
Use a Keyword Ownership Map
Document:
- Primary keywords
- Secondary keywords
- Assigned URLs
- Page type (blog, service, category)
Check this map before creating new pages. This small step prevents a lot of future cleanup.
Audit Regularly
Even with a plan, cannibalization can creep in. Schedule quarterly audits to:
- Check new pages
- Reassign primary pages
- Update content structure
This keeps your site healthy and rankings stable.
Final Thoughts
Content cannibalization is not a content problem — it’s a planning problem.
Fixing it at scale is not about deleting pages blindly. It’s about:
- Identifying the right primary pages
- Merging or differentiating content
- Strengthening internal links
- Creating a system to prevent future issues
With a clear strategy, your website will:
- Rank more consistently
- Improve traffic and clicks
- Provide a better experience for users
Fix it systematically, and your content will work smarter, not harder.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
0 / 5. 0