Every time you browse the internet, there’s a silent exchange of messages between your browser and the server hosting the website. These messages, known as HTTP status codes, are crucial in ensuring smooth communication. Whether you’re accessing a webpage, encountering an error, or being redirected, these codes tell you exactly what’s going on behind the scenes.
HTTP status codes help determine whether the page is accessible, what went wrong, and what action you need to take. Understanding these codes is essential for anyone managing websites, troubleshooting online issues, or looking to improve their website’s performance. In this article, we will explain HTTP status codes in detail and provide a comprehensive list to help you understand their meanings and implications better.
What are HTTP status codes?
In simple terms, HTTP status codes are messages that a server sends to a browser to indicate the result of a request. When you type a website address into your browser, it sends a request to the server. In return, the server sends back a three-digit HTTP status code, indicating whether the request was successful or if there was an issue.
These codes act as a form of communication between browsers and servers. Think of them as “signals” that tell browsers how to handle the requested page.
Understanding HTTP status codes is not just for technical people. If you manage a website, knowing these codes is crucial for identifying errors, reducing website downtime, and ensuring a smooth user experience—all of which contribute to improving search engine rankings.
John Mueller explained that HTTP status codes are the first thing Google checks when crawling the content.
He was posed with the question:
‘Wondering if Google checks status codes before anything else, like before rendering content?’
In response, Mueller confirmed that Google does check the status codes before rendering or indexing content. Google checks for a ‘200’ status code before proceeding with crawling any further. A 200 status code indicates to Google that it is crawling a valid page and there might be content worth indexing on it. Here is the video on different errors that Google may find & report while crawling your website

Why do HTTP Status Codes Matter for SEO?
You may not always see HTTP status codes when browsing a webpage, but they are incredibly important behind the scenes. If a webpage is unavailable, for example, the browser will receive an HTTP status code showing the issue, such as a server error or a missing page.
These codes impact Search Engine Optimization (SEO) significantly. Search engines like Google rely on HTTP status codes to detect errors, crawlability issues, and even reduce website downtime. When Google crawls a website, it first checks the HTTP status code before anything else.
For instance, a 200 OK status code signals to Google that the page is valid, functional, and ready to be indexed. Pages that return this code are considered crawlable and indexable, which is essential for ranking in search engines. If a page returns a 404 or 500 status code, it can negatively affect your SEO.
John Mueller, a Google Search Advocate, explained that Google checks these codes before proceeding to crawl and index the content. If Google encounters a 200 status code, it indicates that the page is healthy, and the content may be worth indexing. You can watch his video on the errors that Google might find and report while crawling your website.
List of HTTP Status Codes
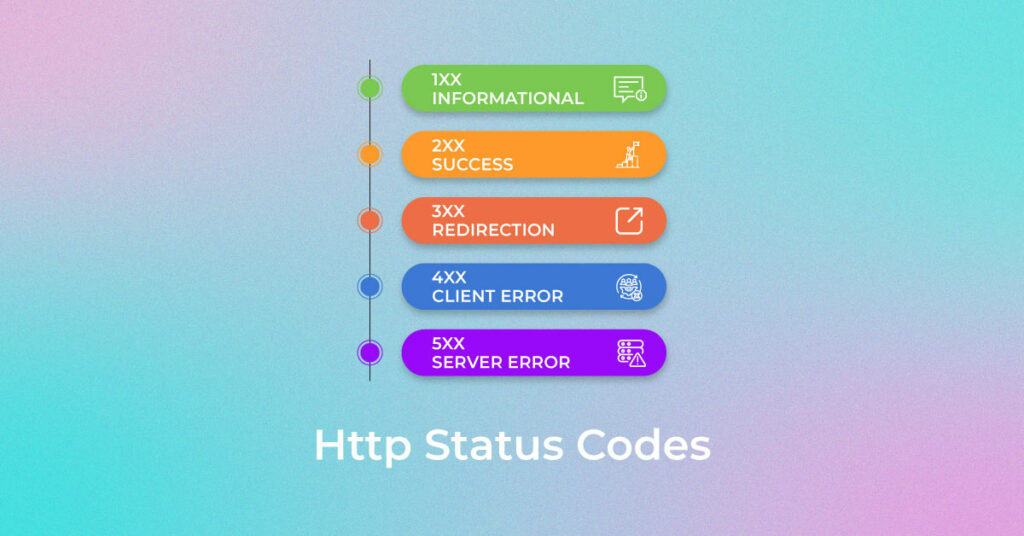
HTTP status codes are divided into five groups based on their first digit. Each group signifies a different type of response from the server.
- 1xx HTTP status codes group (Informational): These codes tell you that the server has received and is processing your request.
- 2xx HTTP status codes group (Success): These codes mean your request was successful.
- 3xx HTTP status codes group (Redirection): These codes tell you that further action is needed to complete the request (usually a redirect to a new URL).
- 4xx HTTP status codes group (Client Error): These codes indicate that there was an issue with the request you sent.
- 5xx HTTP status codes group – (Server Error): These codes mean there’s a problem on the server side.
Here’s an interesting and detailed image that will help you understand the different types of HTTP response codes you might encounter when accessing a webpage.
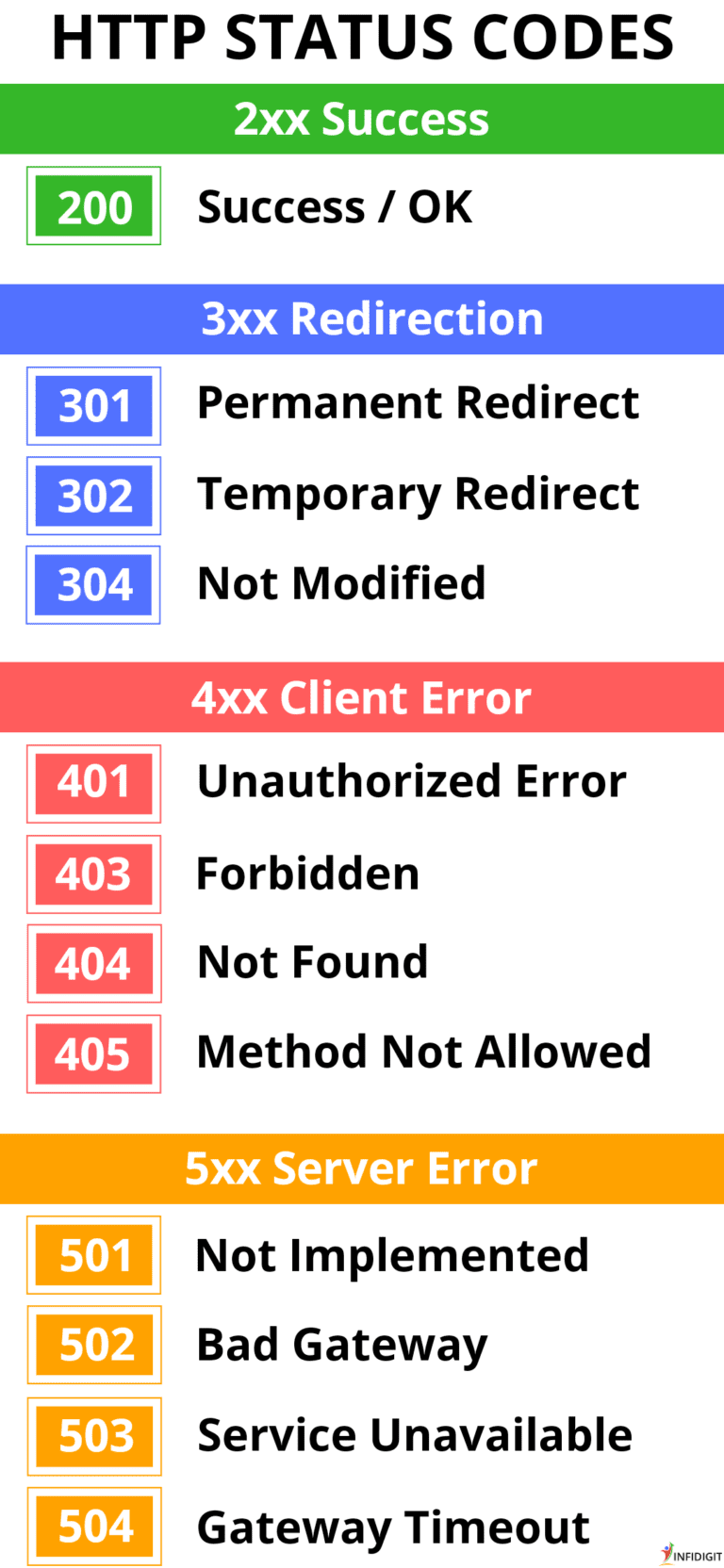
List of HTTP Status Codes and What They Mean
HTTP status codes are categorized into five main groups, each representing a different type of response from the server. Below is a breakdown of each group and what the various status codes within them signify.
1xx HTTP response status codes group
100 Status Code: Continue
The 100 Continue status code means that the server has received the initial part of the request and is ready to continue processing. It’s often used when the client is sending large amounts of data, allowing the server to confirm that it’s prepared to handle the entire request before the data is fully transmitted.
Example: This might occur when submitting large files in a POST request.
101 Status Code: Switching Protocol
The 101 Switching Protocols status code indicates that the client requested a protocol change (e.g., upgrading from HTTP to HTTPS or switching to WebSocket) and the server agrees. This ensures that communication between the client and server can occur using a more secure or appropriate protocol.
Example: Upgrading from HTTP to HTTPS for security purposes.
102 Status Code: Processing
This code signals that the server has received the request, but it’s still being processed. This is common for long-running tasks that take time to complete. It tells the client to wait while the server processes the request.
Example: Used when executing large database queries or processing complex operations.
103 Status Code: Early Hints
The 103 Early Hints status code tells the client about preloaded resources (such as images, scripts, or CSS files) before the full response is ready. This allows the browser to start loading resources early, improving page load times.
Example: Preloading resources for faster rendering while waiting for the final response.
2xx HTTP response status codes group
These codes indicate that the request was successfully received, understood, and processed by the server.
201 Status Code: Created
A 201 status code indicates that a new resource has been successfully created as a result of the client’s request. It’s commonly used for POST requests, such as creating a new user or submitting a form.
Example: After submitting a form to create a new blog post, you may see this status code.
202 Status Code: Accepted
The 202 Accepted status code means the server has received and accepted the request, but the process is not yet complete. It’s useful for asynchronous tasks that take time to finish.
Example: A background task for processing an order might return this code, indicating that the order is in progress but not yet finalized.
203 Status Code: Non-Authoritative Information
The 203 status code is returned when the server successfully processes the request, but the response is based on third-party information, not the origin server.
Example: When fetching data from a cache instead of the original server.
204 Status Code: No Content
A 204 No Content status code tells the client that the server has successfully processed the request, but there is no content to send in the response body. This often happens after a successful action, such as form submission.
Example: After submitting a contact form where no additional data needs to be returned.
205 Status Code: Reset Content
The 205 Reset Content status code instructs the client to reset the document’s state. It’s typically used in forms to clear the form fields after submission.
Example: After submitting a form with errors, the server might send a 205 response to reset the form fields.
206 Status Code: Partial Content
The 206 Partial Content status code indicates that the server is returning part of the requested resource. This is often used for large files that are downloaded in chunks.
Example: Downloading a large video file in multiple parts.
207 Status Code: Multi-Status
This code indicates that the server has returned information from multiple resources in a single response, typically used in batch processing operations.
Example: A single request that modifies multiple resources, such as adding new records to a database.
208 Status Code: Already Reported
This code is used to avoid redundant reporting when the same resource has been listed previously. It helps improve efficiency, especially in collaboration environments.
Example: In a collaborative environment, when multiple users edit the same file, this status code prevents redundant enumeration.
226 Status Code: IM Used
The 226 IM Used status code indicates that the server has fulfilled the request and applied some modifications to the resource during the process, such as applying an Instance Manipulation (IM) operation.
Example: Applying image optimization during an HTTP GET request.
3xx HTTP response status codes group
The 3xx range of HTTP status codes is used for redirection. These codes indicate that the client must take additional actions to complete the request.
300 Status Code: Multiple Choice
The 300 Multiple Choices status code indicates that the server has multiple options for the requested resource, but it does not specify which one to choose. The client may have several ways to access the same resource, such as different formats or languages. The server leaves the decision to the client or user.
Example: Imagine visiting a website that supports both English and Spanish versions. When you request the resource, the server responds with a 300 Multiple Choices status code, listing the available language versions. The user can then select which version to view.
301 Status Code: Permanent Redirection
The 301 Moved Permanently status code indicates that the requested resource has been permanently moved to a new URL. Both browsers and search engines will now use the new location for future requests. This code is important for maintaining SEO integrity, as search engines update their indexes to reflect the new URL, ensuring that search rankings are preserved.
Example: If a website undergoes a major restructuring and a page’s URL changes permanently, the server responds with a 301 status code, ensuring that any links or search engine results pointing to the old URL will redirect to the new one.
SEO Tip: When using a 301 redirect, it’s important to implement it properly to avoid 404 errors and ensure your SEO rankings are preserved.
Here is what Google’s John Mueller has to say on how long it will take to rank a new URL after doing a 301 redirect to the old URL:

302 Status Code: Temporary Redirection
The 302 Found status code (formerly called “Moved Temporarily”) tells the client that the requested resource has temporarily moved to a different URL. Unlike the 301 status code, this change is not permanent, and future requests should use the original URL.
Example: A webpage might be temporarily moved during maintenance or for special events. For instance, if an e-commerce site has a special sale on a subdomain, a 302 redirect can be used to direct users to a temporary location.
303 Status Code: See Other
The 303 See Other status code tells the client to retrieve the requested resource from a different URL using a GET request. This is commonly used after a POST request to indicate that the response is available at another location and that a GET request should be used to fetch it.
Example: After submitting an online form (POST), the server might return a 303 status code to inform the client that the result of the submission is available at another URL via a GET request.
304 Status Code: Not Modified
The 304 Not Modified status code indicates that the requested resource has not changed since the last time it was requested. The client can continue using the cached version of the resource, saving bandwidth and reducing load times.
Example: A user revisits a website and their browser sends a request for a resource. The server checks the last modification date of the resource and, if it hasn’t changed, returns a 304 status code to inform the browser to use the cached version.
305 Status Code: Use Proxy (Deprecated in HTTP/1.1)
The 305 Use Proxy status code was used to indicate that the client must access the requested resource through a specified proxy. However, this status code was deprecated in HTTP/1.1 and is no longer used in modern web development. Other codes, such as 407 (Proxy Authentication Required), are used in its place.
307 Status Code: Temporary Redirect
The 307 Temporary Redirect status code indicates that the resource has temporarily moved to a new URL. Unlike a 302 redirect, the 307 code specifies that the HTTP method used for the request (e.g., POST or GET) should remain unchanged when following the redirect.
Example: If an API endpoint temporarily moves but the server doesn’t want to change the request method, it will return a 307 status code to ensure that the client uses the same HTTP method to fetch the resource from the new location.
308 Status Code: Permanent Redirect
The 308 Permanent Redirect status code is similar to the 301 code, but it ensures that the HTTP method used in the original request is preserved when redirected to the new URL.
Example: A REST API endpoint that permanently moves to a new URL and wants to ensure that POST requests are also forwarded as POST requests would return a 308 status code.
4xx HTTP response status codes group
The 4xx range is reserved for client-side errors. These errors usually occur when there is an issue with the request sent to the server.
400 Status Code: Bad Request
The 400 Bad Request status code indicates that the server could not understand the request due to malformed syntax. This typically happens due to issues like missing parameters, incorrect formatting, or invalid query syntax.
Example: If a user sends a request with an invalid URL (like a malformed query string), the server will respond with a 400 error, prompting the user to correct the issue.
401 Status Code: Unauthorized Error
The 401 Unauthorized status code is returned when the client must authenticate before accessing the requested resource. This error occurs when the request is missing valid authentication credentials, or the credentials provided are not sufficient.
Example: When attempting to access a secure page on a website that requires login credentials, the server will return a 401 status code if the user hasn’t logged in or provided invalid credentials.
402 Status Code: Payment Required
The 402 Payment Required status code was originally intended to indicate that the client needs to pay for access to the resource. However, it is not widely used and is reserved for future use.
403 Status Code: Forbidden Error
The 403 Forbidden status code indicates that the server understands the request, but refuses to authorize it. This could be because the user doesn’t have the necessary permissions or access rights to the resource.
Example: If a user tries to access a protected page (like an admin dashboard) without the correct permissions, the server will return a 403 status code.
404 Status Code: Page Not Found
The 404 Not Found status code occurs when the requested resource cannot be found on the server. This is one of the most common errors encountered on the web, usually indicating that the URL was typed incorrectly, or the page was removed.
Example: If a user tries to access a non-existent page, such as example.com/about-us, they’ll see a 404 error because the page does not exist.
SEO Tip: Properly handling 404 errors can help improve user experience and SEO. It’s advisable to create a custom 404 page and manage broken links to maintain the site’s SEO ranking.

405 Status Code: Method Not Allowed
The 405 Method Not Allowed status code occurs when the client sends a request using an HTTP method that the resource does not support. For example, trying to submit a form with a GET request instead of POST will trigger this error.
Example: If a form is designed to be submitted via POST but a user tries to access it via a GET request, the server will respond with a 405 error.
406 Status Code: Not Acceptable
The 406 Not Acceptable status code is returned when the server is unable to provide a version of the resource that meets the client’s preferences, such as language or media type. This happens when the server can’t match the content with what the client accepts.
Example: If a client requests a page in French but the server only has the page available in English, it might return a 406 error.
407 Status Code: Proxy Authentication Required
The 407 Proxy Authentication Required status code is similar to the 401 Unauthorized error, but it indicates that the client must authenticate with a proxy server before the request can proceed.
Example: A client behind a corporate firewall or proxy server might see this error if the server requires authentication to pass the request through the proxy.
408 Status Code: Request Timeout
The “408 Request Timeout” status code is returned when the client’s request took too long to complete, and the server decides to close the connection. This typically happens when the client does not send a request or complete a request within a certain time frame. Servers use this to prevent idle connections from consuming server resources. In many cases, a timeout might occur if the client is uploading a large file and it takes longer than expected to complete the operation.
Example: If you’re trying to upload a 10MB file over a slow connection and it takes too long, the server may close the connection and return a 408 error, asking you to resend the request.
409 Status Code: Conflict
The “409 Conflict” error occurs when a request cannot be completed because it conflicts with the current state of the server or resource. This can happen when the client is attempting an operation that cannot be performed due to conflicting information. The conflict may be due to data changes made by another client or system.
Example: If two users try to update the same database record at the same time, the second update attempt might trigger a 409 error, indicating a conflict with the data.
410 Status Code: Gone
The “410 Gone” status code indicates that the requested resource has been permanently removed from the server and is no longer available, with no forwarding address. Unlike a “404 Not Found” error, which could mean that the resource is temporarily unavailable, a 410 error means the resource has been intentionally and permanently deleted. This helps inform users and search engines that the resource will not return.
Example: If an online store deletes a product page permanently and does not redirect it elsewhere, users trying to access that page will receive a 410 error.
411 Status Code: Length Required
A “411 Length Required” error is returned when the server expects the client to include a Content-Length header in the request but it is missing. This header specifies the size of the request body in bytes. If the client fails to provide this information, the server cannot process the request properly and rejects it with a 411 error.
Example: When submitting a POST request with data (e.g., form data or JSON), the client needs to specify how much data is being sent by including the Content-Length header. If omitted, the server responds with a 411 status.
412 Status Code: Precondition Failed
The “412 Precondition Failed” status code indicates that one or more conditions provided by the client in the request headers could not be satisfied by the server. These conditions are often specified using the If-Match, If-None-Match, If-Modified-Since, or If-Unmodified-Since headers. If the condition is not met, the server will return this error.
Example: If a client sends a request to update a resource with an If-Match header that contains an outdated version of the resource, the server will return a 412 error, indicating the precondition has failed.
413 Status Code: Payload Too Large
The “413 Payload Too Large” status code occurs when the request is too large for the server to process. This is typically seen when the client is sending a request with a body that exceeds the maximum allowed size configured on the server. Servers often limit the size of the data they can handle to prevent abuse or resource exhaustion.
Example: Uploading a file that exceeds the server’s size limit (e.g., attempting to upload a 100MB file to a server that allows a maximum of 10MB) would result in a 413 error.
414 Status Code: URL Too Long
The “414 URI Too Long” status code is returned when the URL of the request exceeds the maximum length the server can process. URLs are subject to length limitations, and if the client sends a request with an excessively long URL, the server will reject it. This error often arises when the URL contains a large number of query parameters or data.
Example: A search URL with many parameters or a URL that encodes large amounts of data could exceed the server’s length restrictions, triggering a 414 error.
415 Status Code: Unsupported Media Type
The “415 Unsupported Media Type” error indicates that the server cannot process the request because the media type (e.g., content type) is not supported. The client’s request is typically accompanied by a Content-Type header, which specifies the format of the data being sent (e.g., application/json, text/html). If the server doesn’t support the specified format, it will return a 415 status code.
Example: If you try to upload an image in a format like .webp to a server that only accepts .jpg or .png, the server would return a 415 error due to unsupported media.
416 Status Code: Range Not Satisfiable
The “416 Range Not Satisfiable” status code occurs when the Range header sent in the request specifies a range of bytes that is outside the bounds of the file or resource. If the client requests a range that exceeds the file size or is invalid, the server returns this error to indicate it cannot fulfill the request.
Example: If a client requests the first 1000 bytes of a file, but the file is only 500 bytes long, the server will return a 416 error because the requested range cannot be satisfied.
417 Status Code: Expectation Failed
The “417 Expectation Failed” status code is returned when the server cannot meet the expectations specified by the client in the Expect header. The Expect header allows the client to set certain expectations (e.g., Expect: 100-continue), and if the server is unable to fulfill these expectations, it will return a 417 error.
Example: If the client sends a Expect: 100-continue header but the server cannot process the request due to internal issues, it will respond with a 417 error.
418 Status Code: I’m a teapot
The “418 I’m a Teapot” status code is part of an April Fools’ joke in the “Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol” (HTCPCP). It humorously indicates that a teapot cannot brew coffee. While not meant for real-world usage, this status code has become a well-known part of internet culture.
Example: Sending a request to a server that supports HTCPCP to brew coffee with a teapot would return a 418 status code.
421 Status Code: Misdirected Request
The “421 Misdirected Request” status code is returned when a request is sent to the wrong server, and the server cannot process it because it is not configured to handle the request. This typically occurs in environments with multiple servers that serve different purposes.
Example: If a client sends a request to the wrong server in a load-balanced environment, the server will return a 421 error.
422 Status Code: Unprocessable Entity
The “422 Unprocessable Entity” status code is returned when the server understands the content of the request but cannot process it due to semantic errors. This often occurs when data in the request is valid in structure but fails validation rules (e.g., missing required fields or incorrect data format).
Example: Submitting a form with incomplete or invalid data (e.g., a date in the wrong format) could result in a 422 error.
423 Status Code: Locked
The “423 Locked” status code indicates that the requested resource is locked and cannot be accessed or modified at the moment. This often occurs when a resource is being edited or is in use by another process.
Example: If a user is editing a document and another user tries to access it, the server may return a 423 error indicating that the document is locked.
424 Status Code: Failed Dependency
The “424 Failed Dependency” status code is used when a request fails due to the failure of a preceding request that it depends on. This is often seen in WebDAV or similar protocols where the successful execution of one request depends on the success of another.
Example: If a DELETE request fails, a subsequent request that depends on the deleted resource will return a 424 error.
425 Status Code: Too Early
The “425 Too Early” status code is used to indicate that the server is not ready to process a request because it was received too early. This can help prevent issues like replay attacks or race conditions that could arise if the request is processed prematurely.
Example: A client trying to process a request too soon after a previous request, potentially causing unintended consequences, would result in a 425 error.
426 Status Code: Upgrade Required
The “426 Upgrade Required” status code indicates that the client must upgrade to a different protocol to access the requested resource. This could be to a newer version of HTTP or another protocol entirely (e.g., switching from HTTP/1.1 to HTTP/2).
Example: If a server requires HTTP/2 for certain operations, but the client is using HTTP/1.1, the server will return a 426 error.
428 Status Code: Precondition Required
The “428 Precondition Required” status code indicates that the server requires certain conditions to be met before processing the request. This is typically used in scenarios where operations should only be performed if specific preconditions are met (e.g., ensuring a resource hasn’t changed).
Example: Before updating a document, the client may need to ensure that the document has not been modified since the last request by including an If-Match header. If this condition is not met, a 428 error is returned.
429 Status Code: Too Many Requests
The “429 Too Many Requests” status code is returned when the client has sent too many requests in a given time period and is being rate-limited. This is often used to prevent abuse or excessive load on the server.
Example: If you hit an API rate limit by sending too many requests in a short time, the server will return a 429 error, and you may also receive a Retry-After header with a time when you can retry the request.
431 Status Code: Request Header Fields Too Large
The “431 Request Header Fields Too Large” status code is returned when the request’s header fields (e.g., cookies or HTTP headers) exceed the server’s size limits.
Example: If a client sends a request with very large cookies or headers, causing the server to exceed its size limit for headers, a 431 error will be returned.
451 Status Code: Unavailable For Legal Reasons
The “451 Unavailable For Legal Reasons” status code indicates that the requested resource cannot be accessed due to legal restrictions. This may occur if the content is blocked in certain jurisdictions due to censorship, legal disputes, or government regulations.
Example: A streaming service might block access to a movie in certain countries due to legal issues, returning a 451 error when users attempt to access it from those locations.
5xx HTTP response status codes group
500 Status Code: Internal Server Error
The “500 Internal Server Error” indicates that the server encountered an unexpected condition or issue that prevented it from fulfilling the request. This error does not specify the exact problem but points to an internal issue within the server, such as a misconfiguration or a server-side failure. It typically means the problem lies with the server itself, requiring further investigation by the server administrator or technical team.
Example: If a website experiences a sudden software crash or a malfunctioning server-side script, users trying to access the site may see a 500 error. The root cause might be a misconfigured script, insufficient server resources, or an issue with the server’s infrastructure.
501 Status Code: Not Implemented
The “501 Not Implemented” error occurs when the server does not recognize the request method used by the client and is unable to support it. This can happen when a client sends a request using a method (such as PUT, DELETE, or PATCH) that the server is not configured to handle. Essentially, the server cannot process the request using the specified method.
Example: A client sends a DELETE request to a server, but the server does not support or allow the DELETE method for the requested resource. As a result, the server responds with a 501 error.
502 Status Code: Bad Gateway
The “502 Bad Gateway” error occurs when a server, acting as a gateway or proxy, receives an invalid response from an upstream server while trying to fulfill a request. This error indicates a communication failure between servers, where the gateway server could not get a valid response from the upstream server it was trying to access.
Example: If you’re using a reverse proxy (e.g., Nginx or Apache) that forwards requests to a backend web server, and the backend server returns an invalid or no response, the proxy server will return a 502 error. This is common in server-side failures, like a backend database going down.
503 Status Code: Service unavailable
The “503 Service Unavailable” status code is returned when the server is temporarily unable to process the request. This typically happens when the server is overloaded or undergoing maintenance. It’s a temporary condition, and the server should return to normal operation once the issue is resolved.
Example: If a popular website experiences high traffic, it may overload the server, leading to a 503 error. Similarly, during scheduled maintenance or updates, users trying to access the site may encounter this error.
504 Status Code: Gateway Timeout
The “504 Gateway Timeout” error occurs when a server acting as a gateway or proxy does not receive a timely response from another server it is trying to access in order to load a web page or fulfill a request. This often happens when the upstream server takes too long to respond, causing the gateway server to timeout.
Example: If a user tries to access a website that requires data from a third-party service, and that third-party service is slow to respond or unavailable, the gateway server will return a 504 error, indicating that the timeout was caused by the upstream service.
505 Status Code: HTTP Version Not Supported
The “505 HTTP Version Not Supported” error occurs when the server does not support the version of the HTTP protocol used in the client’s request. This error typically arises when the client uses an outdated or unsupported HTTP version that the server cannot process.
Example: If a client sends a request using HTTP/1.0 but the server only supports HTTP/1.1 or HTTP/2, the server will return a 505 error because it cannot handle the older version.
506 Status Code: Variant Also Negotiates
The “506 Variant Also Negotiates” status code indicates that the server has an internal configuration error. It typically happens when a server attempts to select a variant of the requested resource but encounters a problem in the content negotiation process. The error occurs when the server cannot determine the appropriate variant resource.
Example: A server misconfiguration, such as when multiple resources are set to negotiate content but one of them is also configured to perform content negotiation itself, leading to a conflict that results in a 506 error.
507 Status Code: Insufficient Storage
The “507 Insufficient Storage” error indicates that the server does not have enough storage space to complete the request. This typically happens when the server runs out of storage or resources needed to fulfill the operation, such as when the server cannot write to the file system or database.
Example: If a server running a file-sharing application runs out of disk space while uploading a new file, it may return a 507 error indicating insufficient storage.
508 Status Code: Loop Detected
The “508 Loop Detected” status code occurs when the server detects an infinite loop while processing a request. This usually happens when a request is repeatedly forwarded between multiple resources without ever reaching its destination, causing the server to detect a processing loop.
Example: If a URL is incorrectly configured to redirect to itself or another URL that redirects back to the original, an infinite loop will occur, and the server will return a 508 error.
510 Status Code: Not Extended
The “510 Not Extended” error indicates that the server requires additional extensions or features to fulfill the request. The current request lacks the necessary extensions or features, meaning the server cannot process it successfully without further modifications or additions.
Example: If the server requires specific headers or protocols to process a request but the client does not provide them, the server may return a 510 error.
511 Status Code: Network Authentication Required
The “511 Network Authentication Required” error occurs when the client must authenticate with the network before the server will allow access. This is often seen with captive portals, such as those in public Wi-Fi networks, where the user must authenticate or log in before they can access the internet.
Example: A user connects to a public Wi-Fi network and tries to visit a website, but they receive a 511 error indicating they need to complete a login or authentication process before they can proceed.
Tools for Checking HTTP Status Codes
There are several tools available to help you check the HTTP status codes of your website’s pages, which is crucial for monitoring site health and optimizing SEO. These tools provide insights into server responses, identifying issues like broken links, redirects, or inaccessible pages. Here are some popular tools for checking HTTP status codes:
1. Google Search Console:
Purpose: Google Search Console offers a comprehensive view of how Googlebot is interacting with your site. It provides detailed reports on crawl errors, server issues, and HTTP status codes. Using this tool, you can easily identify 404 errors, server unresponsiveness, or any issues preventing Google from indexing your pages.
How it helps: Google Search Console will alert you to pages that have issues, such as “404 Not Found” errors or “500 Internal Server Errors.” You can use this information to resolve problems that may hinder your site’s search engine rankings.
2. Screaming Frog SEO Spider:
Purpose: Screaming Frog is a powerful desktop tool that crawls your website, similar to how a search engine bot would. It provides a comprehensive analysis of all the HTTP status codes on your website, including 404 errors, redirects, and other issues.
How it helps: It not only checks for broken links but also helps you analyze the server’s response for each URL, allowing you to find and fix server-side issues. You can also export the results into various formats for detailed reporting.
3. GTMetrix:
Purpose: GTMetrix is a performance analysis tool that provides insights into your website’s loading times, including detailed HTTP status codes and server performance. It offers a comprehensive report on various elements of page speed and response times.
How it helps: It gives you an understanding of how your server responds to requests. This is helpful for detecting HTTP errors such as slow server responses, redirects, or server misconfigurations that affect performance. It also provides suggestions for improving your website’s speed and server response time.
4. Pingdom:
Purpose: Pingdom is a popular website monitoring tool that helps you check your site’s uptime, performance, and server response. It offers HTTP status code checks along with a detailed performance report from multiple locations worldwide.
How it helps: Pingdom allows you to monitor the HTTP status codes returned by your website from different parts of the world, ensuring that users from various locations are experiencing optimal load times and server responses. It can also send you alerts if certain pages return errors or slow down.
5. Curl:
Purpose: Curl is a command-line tool that allows you to manually check the HTTP status codes for any website. By entering a URL, you can directly interact with the server and analyze the response.
How it helps: Curl is useful for developers or users with technical knowledge who need to check the response from a server for debugging or troubleshooting. By adding flags (e.g., -I to get header information), you can get detailed server responses, including HTTP status codes, headers, and more.
6. Ahrefs:
Purpose: Ahrefs is a comprehensive SEO toolset that provides detailed audits of your website, including a breakdown of HTTP status codes for each page. It helps you monitor broken links, redirect chains, and other server-side issues that could impact SEO.
How it helps: Ahrefs crawls your entire website, identifies HTTP errors such as 404s or 500s, and generates reports. It can also identify other SEO-related issues, such as slow-loading pages or poor server responses, which can negatively impact your site’s ranking.
These tools are essential for diagnosing server issues, ensuring a smooth user experience, and maintaining good SEO practices.
Now that you are familiar with the most common HTTP errors, you should have a good basis for troubleshooting issues with your web servers or applications. If you come across any error codes that were not mentioned above, feel free to discuss them in the comments section.
FAQs about HTTP Status Codes
What are HTTP Status Codes?
HTTP status codes are three-digit numbers used in the HTTP protocol to indicate the outcome of a client’s request to a web server. They help communicate whether the request was successful, encountered an error, or requires further action. Understanding these HTTP protocol status codes is essential for diagnosing website issues and ensuring smooth user experiences.
Why are HTTP Status Codes Important?
HTTP status codes play a crucial role in helping search engines and browsers understand the state of a webpage. These HTTP response codes assist in diagnosing website issues, ensuring proper indexing, and improving user experience. By identifying errors like broken links or redirects, they help maintain website performance and SEO effectiveness.
What is the Difference Between 2xx and 3xx Status Codes?
2xx codes represent successful requests, while 3xx codes indicate redirects. 2xx confirms the server processed the request, and 3xx informs the client that the resource has been moved or redirected.
How Do I Fix a 403 Forbidden Error?
A 403 Forbidden error occurs when a server blocks access to a resource due to insufficient permissions. To fix this, check and adjust file or directory permissions, update your .htaccess file, or modify security settings. If the issue persists, contact your hosting provider for assistance. Understanding web server status codes like 403 helps diagnose and resolve such access issues effectively.
How Can I Check HTTP Status Codes for My Website?
You can check web page status codes using various methods, including browser developer tools, online status checkers, and website crawlers. Tools like Screaming Frog, Google Search Console, and third-party HTTP header checkers help identify status codes, allowing you to diagnose errors and ensure smooth website performance.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
3.1 / 5. 11











2 thoughts on “HTTP Status Codes: List of HTTP Response Status Codes”
Just learning about HTTP codes…
Thanks. Read our latest posts for more updates.