Google has always focused on delivering high-quality, relevant content to its users. To support this mission, it introduced the Panda update, an algorithm designed to improve search results by filtering out low-value content. If your website has seen unexpected drops in traffic or rankings, Panda could be one of the reasons. In this blog, we’ll walk you through the update’s impact, signs your site might be affected, and how to recover effectively.

What Is the Google Panda Algorithm Update?
Panda algorithm was one of the significant Google’s algorithm updates launched on February 23, 2011. The primary purpose of this algorithm was to penalize the websites with low-quality content, duplicate content, thin content, low-quality user-generated content, content mismatching search query, high ad-to-content ratio, and many more.
This algorithm, at its initial release, was called the ‘Farmer’ update. Since it mainly focused on the content area of the website. For eg, any website that steals information and creates identical pieces of content. According to Google, Panda’s algorithm update affected 12% of the English search queries.
Unlock higher rankings, quality traffic, and increased conversions through tailored award-winning SEO strategies.
Elevate your web presence by Infidigit’s SEO solutions.
Unlock higher rankings, quality traffic, and increased conversions through tailored award-winning SEO strategies.
Why Did Google Roll Out the Panda Algorithm Update?
In 2009, Google released the “Caffeine Algorithm Update,” which had the capability to index fresh and updated content expeditiously. However, even a not-so-good content present on the website was indexed and ranked. By the end of 2009, two major firms in the USA, ‘Demand Media’ & ‘Answers.com’, released 7000 content pieces per day. The company had a straightforward logic behind it, which was to create a bunch of niches, make it viral via social media, and earn money through ads.
Whereas Demand Media, however, turned out to be bright in tricking Google’s ecosystem. It made an indenture with many freelancers to produce low-quality content on the topics mostly driven by Google. Due to Google’s Caffeine algorithm, Demand’s content ranks higher on SERP now.
And with all these headlines, undoubtedly, Google retaliates by launching the Google Panda algorithm.
Also Read :
Google Panda Update Initial Launch, Rollouts and Timeline
The Google Panda Update saw multiple versions and adjustments after its initial release, each designed to fine-tune how websites were evaluated for content quality. This section covers the key Panda-specific updates, focusing on the timeline of changes and how the algorithm evolved over time.
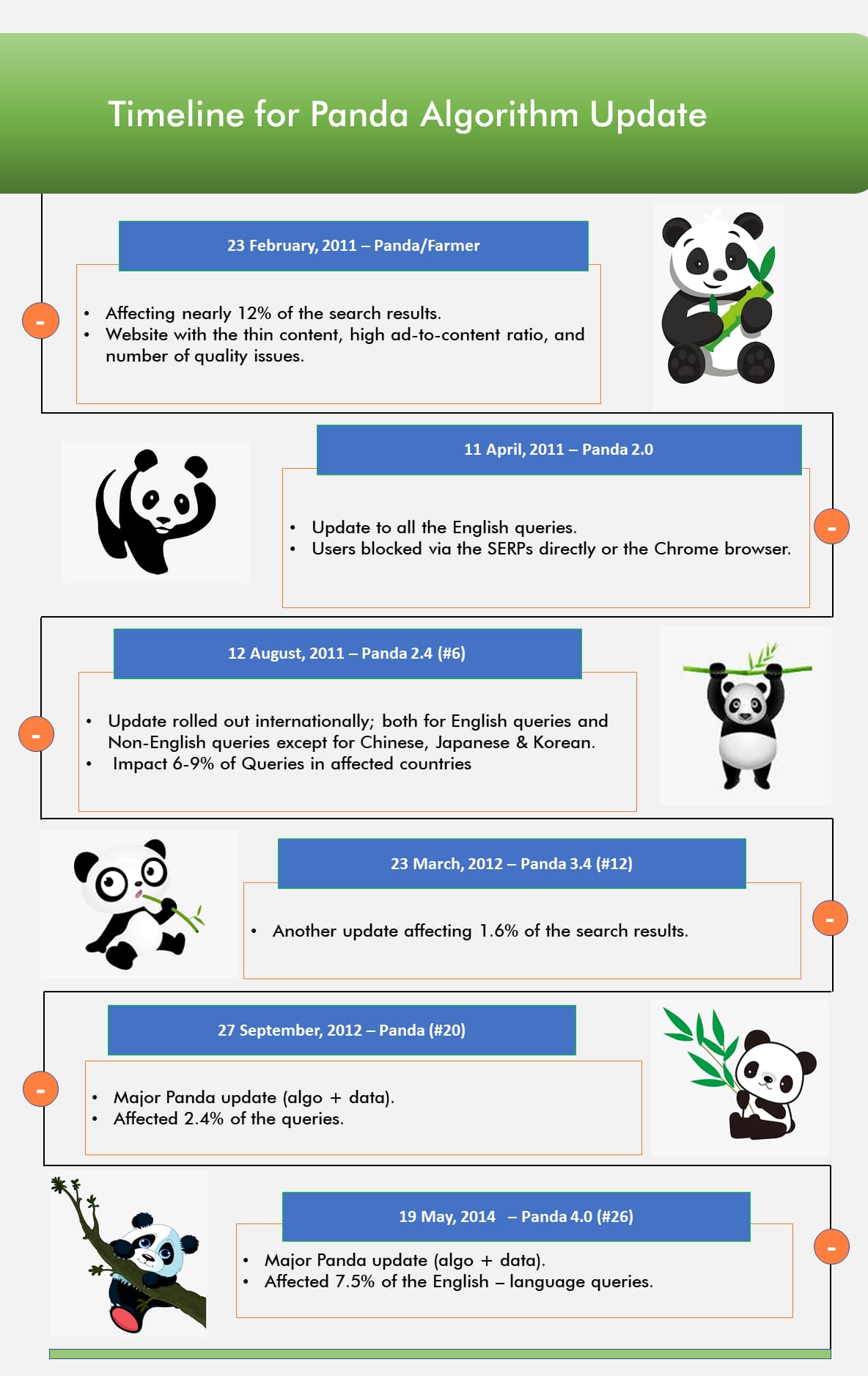
- Feb 23, 2011 – Panda/Farmer: Introduced to target low-quality and thin content websites.
- Apr 11, 2011 – Panda 2.0: Applied the update to all English-language search queries.
- Aug 12, 2011 – Panda 2.4: Expanded the update to international and non-English queries.
- Mar 23, 2012 – Panda 3.4: Rolled out a refresh to improve result accuracy.
- Sep 27, 2012 – Panda (#20): Released a major algorithm and data update.
- May 19, 2014 – Panda 4.0: Launched a significant update with core algorithm changes.
What Triggers a Google Panda Penalty?
-
Thin or Shallow Content
Thin content includes pages with minimal, duplicate, or low-value information. Pages that lack depth, contain generic text, or offer little to no real value to users are often flagged by the Panda Algorithm update. Panda algorithm also affects pages that rely on keyword stuffing, overusing keywords unnaturally to manipulate rankings. Sites with many such pages risk lower rankings due to poor content quality.
-
Duplicate or Spun Content
Duplicate content is the content that is present at more than one site or page. This duplication issue with the content can arise on your website as well. Panda searches for unique information. For example, suppose a website has a large number of pages for real estate, and each page has identical content with just the city name swapped. This is considered a duplicate as per Google’s Panda Algorithm Update. It is like one buys houses in Mumbai, Delhi, Bangalore, and so on.
-
Low-quality Content and Lack of Trust Signals
Google Panda targets websites that publish low-quality content, such as poorly written, duplicate, or keyword-stuffed pages that add little value to users. In addition, sites that lack trust signals, like clear communication, honest claims, or transparent policies, are also at risk. Misleading content, false promises, or vague information can damage user trust and lead to ranking drops. Ensuring your content is original, useful, and credible is key to maintaining visibility in search results.
-
Pages Overloaded with Ads
Pages on the website with very little content and more ads, i.e., paid to advertise.
-
Content Farm
You may have noticed many websites that target nearly every niche. The main objective of such a website is to increase traffic for all prevalent searches. Such a webpage tends to lack authority. The Google Panda algorithm is used in an attempt to lower its ranking and provide value to users.
-
Low-Value Content With Affiliate Links
You may run a website, but you participate in numerous affiliate programmes to earn extra money from it. You may also be promoting paid affiliate programmes on your website. Such elements are a symbol of a poor website, and Google Panda deals with them by lowering its position on the search engines.
-
Sites Frequently Blocked by Users
Is your website irrelevant? Are you reaching out to prospects with direct sales materials, irrelevant content, or emailers? There is a good chance that users will block your site. They use a Chrome browser extension to ban your website. They may even directly block it on search engine results. The Panda algorithm in SEO deals with such sites.
-
Misleading or Unmatched Content
How many times have you clicked on a web page based on its title only to find irrelevant content? Isn’t it quite a few? For example, suppose you visit a website with the title ‘catch heavy discount.’ However, there is no such information on the page, and the website owner’s intention is solely to increase clicks. Google Panda update deals with this.
How to Know If You’ve Been Hit by Panda Update?
Google Panda penalties are algorithmic, so there’s no official warning. However, certain performance drops can signal its impact.
- Sudden Drop in Organic Traffic: A sharp decline in traffic, especially around known update dates, may indicate Panda has affected your site.
- Decline in Keyword Rankings: If multiple pages start losing rankings for key terms, it could be due to low-quality or duplicate content issues.
- Decrease in Indexed Pages: A drop in indexed pages suggests Google may be filtering out thin or non-valuable content from search results.
How to Recover from a Google Panda Penalty?
Recovering from a Panda penalty involves improving overall content quality and user experience. It’s not about quick fixes. Google looks for long-term improvements in site value and trust. Google penalty recovery services can help users recover from such updates.
Audit and Remove Low-Quality Content
Identify and remove thin, duplicate, or outdated pages. Resolve all the grammatical and duplicate content errors. Focus on keeping only content that adds clear value to users.
Improve Content Relevance and Trustworthiness
Rewrite weak pages with accurate, well-structured, and original information. Ensure your claims are supported and your messaging is honest.
Reduce Intrusive Ads
Minimize aggressive or distracting ads that interfere with the main content. A clean, user-friendly layout improves both UX and Panda compliance.
Focus on E-E-A-T Best Practices
Add author details, cite reliable sources, and ensure content reflects real experience and subject knowledge to build credibility with both users and search engines.
Here are some more pointers that need to be considered in order to recover from the Google Panda algorithm update:
- Make the content so informative that users could spend more time on the website, which can immensely reduce the bounce rate of the website
- Increasing click-through rates of the website by writing down the proper title & meta description, relevant data, and many more, as this helps in getting clicks from the SERP
- Resolving lousy content on the website by using different titles/headlines, internal link with proper anchors, fixing broken links.
- Using LSI keywords in the content.
Best Practices to Avoid Panda Penalty in the Future
Preventing a Panda penalty starts with maintaining consistent content quality and delivering genuine value to users. Here are a few key practices to follow:
- Maintain High Content Quality: Focus on original, well-structured, and informative content. Avoid keyword stuffing and ensure content is written clearly for human readers.
- Keep Pages Relevant and Up to Date: Regularly review and update older pages to ensure accuracy. Outdated or irrelevant content can signal low value to search engines.
- Avoid Duplicate and Scraped Content: Ensure every page offers unique content. Avoid copying from other sites and use canonical tags where necessary to prevent duplication issues.
The Google Panda Update marked a major shift in how content quality is evaluated in search rankings. Understanding what triggers a Panda penalty and how to avoid or recover from it is crucial for maintaining long-term SEO success. By focusing on high-quality, original content and avoiding shortcuts like duplicate pages or keyword stuffing, websites can not only stay safe from penalties but also earn better visibility and trust from users. Stay consistent, stay relevant, and always prioritize value for your audience.
FAQs Related to Google Panda Algorithm Update
What Was Google’s Panda Update Also Known as?
Google’s Panda Update was initially nicknamed the “Farmer Update” by the SEO community due to its significant impact on content farm websites that produced large volumes of low-quality content.
What Is the Benefit of Google Panda?
The Panda update improved Google’s ability to surface high-quality, original, and user-focused content while demoting sites with thin or low-value pages. It helped clean up search results and prioritize trustworthy sources.
Can External Backlinks Impact Google Panda Algorithm Penalties?
No, Panda primarily targets on-site content quality, not backlinks. Link-related penalties or evaluations fall under separate systems like Google Penguin or manual actions.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
5 / 5. 1















4 thoughts on “The Ultimate Guide to the Google Panda Update”
I Read This Blog And In This Blog Wonderful Info For panda Update.
Thank you for your feedback.
Thanks for this information
Glad to know that it was useful. Check out our latest posts for more information.