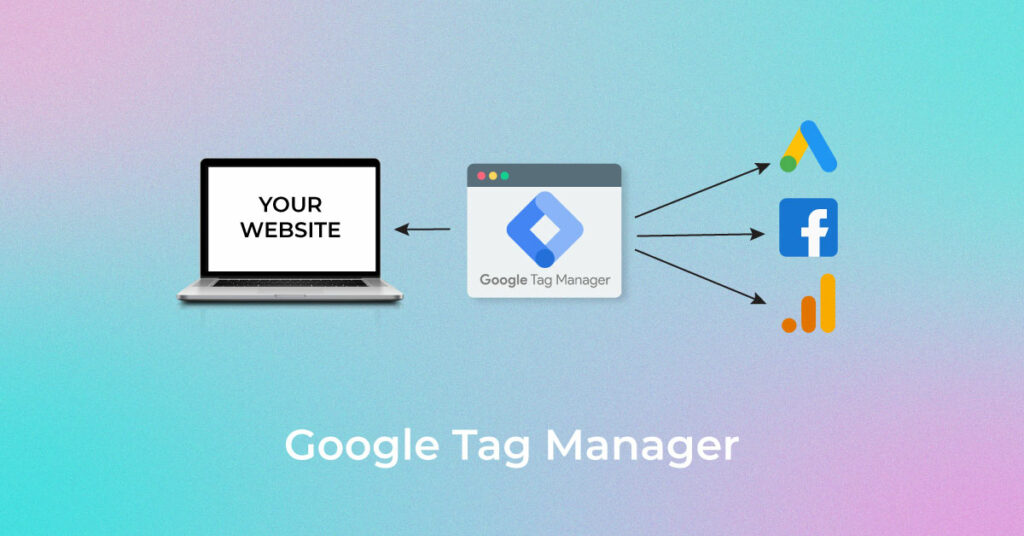
What is Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager or GTM is a web-based Tag Management Platform by Google. It was introduced in October 2012 to make the process of tag management easy & efficient. The tag is a piece of code placed on a Website or App which, when triggered, can send tracking data to third party platforms such as Google Analytics. We can also set a GTM container snippet on Web Applications and AMP pages of the site.
In today’s competitive business environment, measuring and reporting data to gain valuable business & consumer insights is paramount for business survival. The introduction of Google tag manager is considered revolutionary in a way that it has eliminated the need of the developer, at least in terms of tag deployment & management.
How it is Different from Google Analytics
Google Tag Manager (GTM) and Google Analytics (GA) are both Google products used extensively by webmasters. Apart from that, there is no similarity between the two. However, both work in unison and help in tracking and reporting more accessible data. GTM is mostly used for the creation and deployment of tags, whereas Google Analytics is used for monitoring and reporting data. GTM can work well with third party tags such as Crazyegg & Hotjar, making it a versatile tag management system. People do get confused between GA & GTM. They can easily answer what google analytics is but if you ask them about GTM they stutter for words, Even the best SEO companies in India providing the best of SEO services have a hard time using it to its full capacity.
You can check this video below to get an overview of Google Tag Manager

How Google Tag Manager works
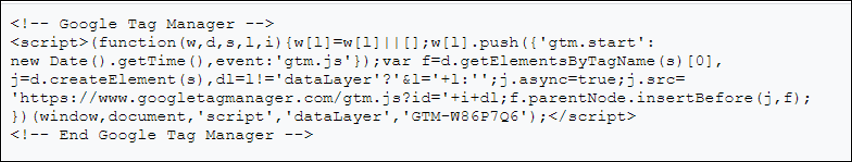
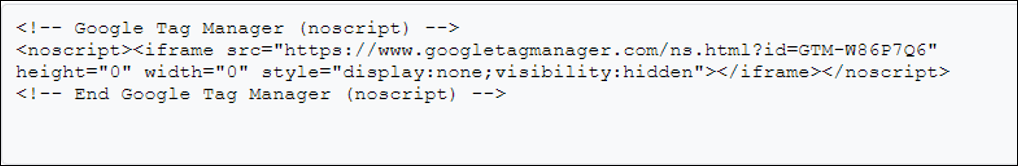
Google tag manager contains a piece of container code that one has to place on all the pages of the website. This code is simply a javascript code that is placed on the head and body sections of the source code. The code placed on the head is a script, and the one on the body is no script iframe code, which acts as a backup for the code placed inside the head tag. Frame code helps to track the non-Javascript users, that is, when a user visits the site from a non-javascript supported browser or device, this code tracks such users.
Head Section code
No Script Code
Once the container code is placed on the website or app, you are ready to collect data from the digital property. You can create several tags in the tag manager right from universal analytics to third party tags like Crazyegg, Hotjar, and so on. One can even have a custom tag by writing a custom javascript code. Updating or deleting the tag in GTM will be updated in real-time on the container code placed on the website. You should configure Trigger Variable for a particular tag to fire so the data is sent to the analytics as intended.
Below you can see a screenshot of a container panel.
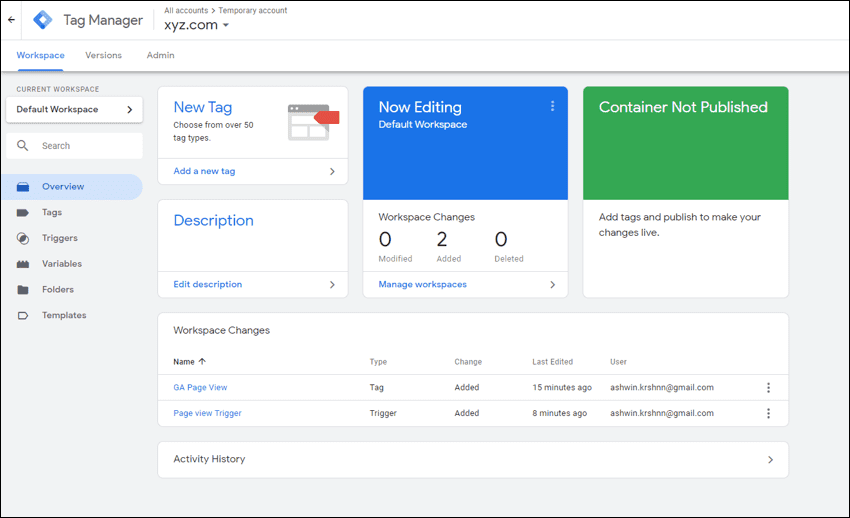
Account name: Temporary Account
Container name: xyz.com
Tag name: “GA page View” (it is defined to trigger on all pages)
Trigger: “Page view Trigger” will listen for event Page View on all pages so the tag fires
This is just a basic configuration, however, one can explore the tool and create more tags, triggers, and variables depending upon the data collection requirement of your project. It may look like advanced technical SEO but mastering it will be helpful for data collection and analysis.
Unlock higher rankings, quality traffic, and increased conversions through tailored award-winning SEO strategies.
Elevate your web presence by Infidigit’s SEO solutions.
Unlock higher rankings, quality traffic, and increased conversions through tailored award-winning SEO strategies.
Benefits of Google Tag Manager
-
Site Speed
With fewer lines of code to be executed and asynchronous loading of the tag, there is a boost on the overall page speed of the website. Before GTM, the only way to track events was to define event-specific javascript code. So, to track the number of events many lines of code were required, which was a drag on the site’s speed. Site speed being an important ranking factors, webmasters were wary of using it.
-
Ease of use & efficiency
With such a simple interface and few guided clicks, one can easily configure & deploy the tags without writing a single line of code. You can consistently add, update, or delete the tags, triggers, and events whenever required hassle-free without even touching the codebase. Efficiency has increased manifold as a marketer can control most of the implementation by themselves.
-
Support Third-Party Tags
GTM supports tags of third party tags such as Facebook pixel, Twitter, Crazy egg & Hotjar. Currently, it supports more than 80 third party tags making it one of the most highly sought-after tag management platforms.
-
Less Dependency on Developer
With the use of a tag manager, the need for the involvement of the developer has reduced significantly. Not to mention, you still need developers to deploy the code in the back-end and to define the data layer. GTM has also allowed developers to focus on essential tasks rather than on writing, inserting, and optimizing the code on every page.
-
Preview and Debugging mode
Error checking has never been easy. You can cross-check your tag in preview mode to see whether the tag is firing and collecting the data or not, before deploying tags on the website. Error checking is crucial as wrong deployment or error in tags can hinder the collection of data. Even if the data is collected, its reliability will be questionable.
-
Version Control
One of the most important features of the tag manager is a version control mechanism. When you add, delete or update the tags, triggers, or any of the variables, a newer version of the workspace is created with new settings. This version is submitted for the changes to take place. However, you can go back to your earlier version at any point and submit the previous configuration for the current use. Version control has given a lot of flexibility to the webmaster at least in terms of tag modification and implementation.
-
Google Tag Assistant
Google Tag Assistant is a Chrome extension available on the Chrome play store. It is mainly used to identify the number of tags present on the site, it can also be used to validate and troubleshoot the installation of the tags. One must enable the tag assistant to see the tags present on the site. The tags are uniquely represented in colour. It specifies if they are working correctly or not. The green colour shows they are up and running. Blue represents something missing in the tag with the missing details highlighted.
Red colour represents a tag not firing at all. It can be due to a significant error that might need an immediate fix. One can also record the tags while browsing through the website to get an in-depth analysis of tag implementation and validation of the Google Analytics configuration.
So now we know what google tag manager is and how important it is for one’s business. I would recommend you go through the google documentation for more information on the Google tag manager.
Components of Google Tag Manager
Tag Manager consists of different components that one has to configure for proper collection and recording of data.
-
Containers
Containers are the place in the GTM account where all the tags defined for the web property is present, it is the central place where all tags reside. A single Google account can have many containers. Usually, businesses use different Containers for different web properties. You can add as many tags as you want in the Container, but it is advisable to add tags that are necessary from a data-gathering point of view. A Container in simple words is similar to ToyBox, which can hold many different toys in it.
-
Triggers
Triggers are listeners of events; they instruct the tag manager to fire the respective tag on the occurrence of a particular event. Without setting the Trigger, the tag will not fire for data collection. You can choose from many built-in events predefined in GTM while creating the tag. Triggers consist of two main components – Events and Filters.
Events are actions such as page view, button click, page scroll, and link click that happen on the pages.
Filters further consist of three components – Variables, Operators, and Values. This trio forms a rule which, when fulfilled on the occurrence of an event, can trigger the condition to fire a tag. This tag can collect the data and pass it on to Google Analytics for storing and processing.
You can also define blocking triggers in the GTM. This is helpful when you do not want the tag to fire on particular pages. The blocking Trigger will be given the priority while firing of the tag.
-
Variables
Variables are simply placeholders of the value whose evaluation is necessary for the firing of Trigger. In general, Variables are represented in a numeric value, but in Tag manager, it is more of String value such as URL, Page name, and so on. Variables can be of two types – built-in and Custom. Built-in variables are the predefined variables available in GTM, and Custom variables are something you can define. Built-in variables for apps are different from website variables.
-
Data Layer
Data Layer is Javascript Object Array, which stores the information from the webpage that is accessed by GTM to check whether a tag has to be fired or not. The data is pushed in the data layer dynamically from the server and is structured in a standard format making it easily readable by GTM. Data Layer is automatically initiated when we place the GTM snippet on the site. Sometimes we want to collect data from a custom event. At that time, defining and pushing the custom data into the data Layer becomes necessary. DataLayer code is always placed ahead of the GTM container code. If the data layer code is placed after the container snippet, any variables declared within will not be available for Google Tag Manager to selectively fire tags on page load.
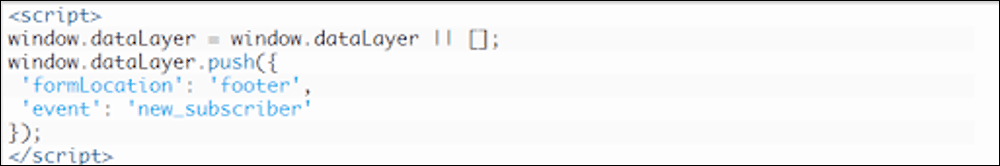
Implementing the Data Layer is critical for tracking. The failure of the data Layer to collect data will affect the GTM functioning. This is because google tag manager is heavily reliant on data Layer to provide the value of the data necessary for firing the tag.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
0 / 5. 0