SEO, as we all know, is a vast, constantly-evolving field of digital marketing that strengthens the brand voice, and boosts website traffic and ROI (return on investment). Its inexpensive yet highly effectual nature has led to its increased use by search marketing professionals who are up to speed with the latest happenings in the field. However, seldom does one wonder about how it all began. Although there is no concrete literature pointing to a specific time when SEO first came into existence, most industry experts believe that it all started in 1991. We have come a long way since, with huge, swanky websites crowding the internet and clamouring for attention from users. Add to this the ever-changing ways of search engines and the result is a quantum shift in the way online search works. This in turn has led to the evolution of search engine optimization (SEO) techniques over the years. If you have forever been curious about what search marketing experts did differently back in the day, read on for a quick trip down the SEO memory lane.
The Birth of the Internet
The number of internet users has skyrocketed in the past few years and is increasing every single day. Users are constantly searching for all the information they need through various devices, and search engines are pulling out all the stops to provide them with the most relevant, contextual results. But have you ever wondered when and how it all began? Remote computers could connect over basic telephone lines with the AT&T commercial modem that was launched in 1958. This was the most nascent form of the internet, with the term ‘internet’ being coined much later in December 1974.
Search Engines
With time came a barrage of online information that needed to be organized and indexed in an efficient way so that its retrieval was uncomplicated and useful. Although Dr. Vannevar Bush, the Office of Scientific Research and Development’s director in the USA, had conceptualized a directory or database for the world’s data in 1945, it was not until 1990 that the first search engine, Archie, was invented by Alan Emtage. It was born out of a school project and indexed FTP (File Transfer Protocol) files based on text.
The discovery of a few other early search engines is as described below:
- Archietext was created by a group of six Stanford University students in February 1993. It later evolved into the search engine, Excite, which was officially introduced in 1995. It worked by sorting online information/content based on the keywords found in it.
- The World Wide Web Wanderer, later called the Wandex, debuted in June 1993 under the leadership of Mathew Grey.
- Aliweb was launched in October 1993 by Martijn Koster, and permitted the submission of webpages by their owners.
- December 1993 saw the unveiling of three search engines – World Wide Web Worm, RBSE spider and JumpStation – that used web robots to crawl various sites.
- 1994 was a big year that witnessed the launch of four popular search engines, namely Yahoo, Alta Vista, Lycos and Infoseek.
- AskJeeves was introduced to the world in April 1997 and later came to be known as Ask.com.
- The domain Google.com was registered in September 1997.
Also Read:
Google Revolution
In 1998, Sergei Brin and Lawrence Page, the creators of Google, published a paper titled ‘The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine’ as part of their research project while studying at Stanford University. In it, they wrote ‘the predominant business model for commercial search engines is advertising. The goals of the advertising business model do not always correspond to providing quality search to users.’ This was what many consider a history-making moment as they went on to elaborate on PageRank, a technology that Google employed to judge how relevant a webpage was to a search query and rank it. It is important to note here that it did so based on content quality and not just the search keyword.
Although Yahoo was the result of a campus trailer project by creators David Filo and Jerry Wang, it soon gained prominence for being a directory of useful sites and internet bookmarks. Web publishers would put their webpages up for scrutiny so that it would index them and make them available to searchers everywhere. In 2000, Yahoo committed a strategic blunder by striking up a partnership with Google to manage its organic search. This in turn led to every search result bearing the ‘Powered by Google’ tag, thereby catching the eye of many a Yahoo user. Thus, Yahoo helped Google script its success story by giving it an early launchpad at the turn of the century.
It is important to note here that there were many reasons for Google’s undeniable success. Until 2000, websites were ranked based on many now-archaic and inadequate practices of bread-crumbing (web links that indicate your site’s structure), and on-page content, among others. Google, however, analyzed on-page and off-page activities side by side before deciding the rank of a webpage in its SERP. SEO professionals around the globe misinterpreted this and considered links to be the end-all of gaining a good spot in Google’s SERPs. Link-building became a rampant black-hat tactic that was addressed by Google in the coming years. The Google Toolbar was launched as an additional feature on the Internet Explorer and showed web publishers their PageRank score, a measure of how important a webpage was.
Besides the aforementioned differentiators that made it a legendary information retriever, Google has always had a reputation for introducing frequent and game-changing updates, the most major of which are the following:
- 2005’s Jagger update ensured that anchor text was no longer as important a factor in determining a webpage’s rank. It also helped Google make great headway in stemming the exchange of random, unsought links.
- 2011’s Panda update was introduced to quash the problem of content farms, i.e. websites that churned out poor-quality, unoriginal and auto-generated content and made money from ads. This update deserves special mention as, after many changes over an extended period of time, it was incorporated into Google’s main algorithm.
- 2012 saw the release of the Penguin update, aimed at tackling dubious, spammy measures that included suspicious linking patterns within websites coupled with anchor text that contained keywords that web publishers intended to rank highly for.
- 2017’s Big Daddy update shed more light on weblinks and the relationship between sites
Google’s world dominance has irked many a search competitor throughout its long epoch. Yahoo, not one to stay beaten after the previous debacle of 2000, tried to undo its misstep by collaborating with Microsoft through a ten-year alliance in 2009. In a bid to loosen Google’s grip on approximately 70% of the American search market, Yahoo decided to have its paid and organic search fuelled by Bing, a derivative of Microsoft Live Search. This however did nothing to shake Google’s numero uno status and only strengthened Bing’s position as the second most popular search engine in the world. Additionally, the ten-year Microsoft and Yahoo partnership ended up being revisited midway, after just five years from its start.
History of SEO & How It has Evolved

The evolution of Google gave rise to changes in tactics used by SEO experts around the world to achieve high search rankings. The following are the most landmark moments in the history of SEO:
- In 1997, the manager of the Jefferson Starship, a popular rock music band, was not too thrilled that their official website was not ranking on the first SERP. This was when the term ‘search engine optimization’ was supposedly coined. Alternatively, it is believed that John Audette, the founder of MMG (Multi-Media Marketing Group), while meeting with Danny Sullivan to convince him to join his company, first used the term. The latter conceived the idea of Search Engine Watch, an SEO news-provider and trend-spotter. A decade later, he founded the very well-known publication, Search Engine Land, after walking away
from Search Engine Watch. - 1998 witnessed the birth of Goto.com, which allowed website owners to bid on the space above the organic search results that were generated by Inktomi. These paid search and sponsored links were also shown adjacent to and below the organic search results. Yahoo finally absorbed Goto.com. This was also the year that MSN entered the search arena with MSN Search.
- In 1999, the first official search marketing event was conducted as part of the Search Engine Strategies (SES) conference.
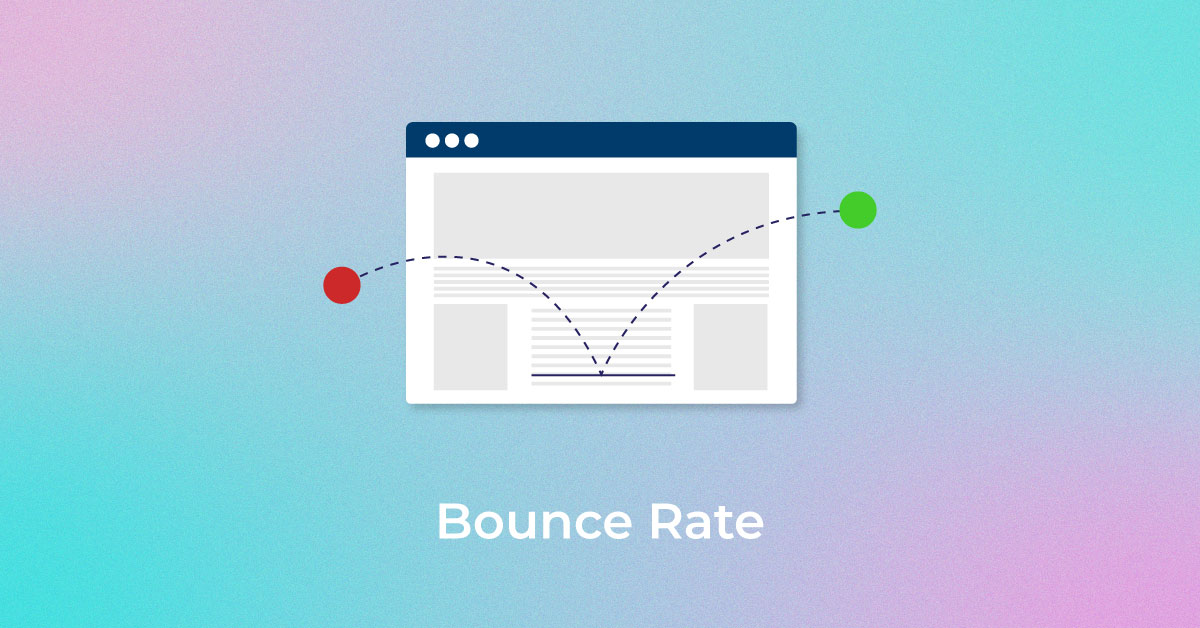
- Google took over YouTube in 2006 for billions of dollars. The latter is highly popular with users with more than a billion of them overall. This led to SEO experts delving deep into video optimization techniques and brands using the video-streaming platform to their advantage to create a strong online voice. Google Webmaster Tools (now called the Google Search Console) and Google Analytics were also launched in the same year, introducing web publishers to a whole new world of possibilities. With them, they could view the search keywords for which their sites ranked highly, errors in crawling or inclusion, user session length, bounce rate and so much more.
- In 2000, Google AdWords was launched. This was also a time when webmasters around the world grew accustomed to the ‘Google Dance’, a period in which the search engine would release major updates to its indexing algorithm, leading to many shakeups in search rankings.
- In 2003, Google took over Blogger.com and started dishing out contextual Google AdWords ads on various publisher websites through its new service, Google AdSense. Although it shaped the blogger revolution of the early 2000s, this plan of action was not a fool-proof one as many websites with mediocre and sometimes even plagiarised content started mushrooming overnight just to garner AdSense revenue.
- In 2004, local search and personalization became major trends, with search results bearing a geographic intent. Users’ previous search patterns and history coupled with their interests allowed Google to custom-make the SERP for every individual, meaning that two users would not see the same search results even if they had entered the same search query.
- In 2005, no-follow tags, meant to push back spammy linking, were invented as a means to better shape PageRank.
- 2007 saw the birth of Google’s universal search wherein, instead of just plain, blue search results on the SERP, other fascinating features like news, images and videos were also included.
- Google Instant was introduced in 2010 – it offered users relevant search query suggestions whenever they would type into the search bar. This was also when Google made it known that the speed of a website was a crucial ranking determinant.
- Google’s Knowledge Graph was unveiled in 2012, resulting in a major step forward in understanding search intent. Here, the internet’s billions of websites can serve as Google’s knowledge database from which it draws the most relevant information in the form of knowledge carousels, boxes, etc.
- A new Google algorithm update, the Hummingbird, was introduced in 2013 with an intent to redefine natural language or conversational search for mobile devices. This has been hailed as the biggest update to Google’s search algorithm since 2001.
- In 2015, the number of mobile-only searchers eclipsed the number of desktop-only users. This was mainly due to the steady climb in mobile phone users who used their smart devices to retrieve useful information while on the move. The availability of robust wireless service providers was another added plus for such people. Thus, Google found it crucial to introduce a search algorithm update that would be mobile-friendly. In the same year, Google acknowledged that RankBrain was a major component of its main search algorithm. It is interesting to note here that this was perhaps the beginning of the AI (Artificial Intelligence) phase for Google as RankBrain uses Machine Learning to understand how it can provide the most relevant search results to user queries.
- In 2016, Google launched the AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages) which instantaneously loaded content. AMPs have been extensively used by media houses.
The Past, Present and Future of SEO
Many search engines have risen and bitten the dust over the years, unlike Google which seems to be going from strength to strength. Here is a comparison of SEO tactics through the ages and the impact they have had on the way search works across devices.
The early days
Earlier in the days, SEO experts were focused more on keywords stuffing and spammy backlinks coupled with increased tagging and comment for ranking higher in search results.
Evolution of SEO
-
All Hail the King, Content!
While the 1990s saw the mindless stuffing of various important keywords into webpage content coupled with backend optimization, these techniques soon came to be frowned upon. This was because Google was devising smarter ways to produce genuine, useful and relevant search results. Today, search intent is of top priority, with Google’s latent semantic indexing techniques producing contextually relevant search results based on user search history and preferences, device, location, etc. Images and videos, which were earlier thought to be unimportant, have now gained prominence, with high-quality images and video content helping webpages rank better on Google.
Note: Matt Cutts of Google has also mentioned “great content has to be the foundation of any good site”
-
Social Media Marketing
The social media boom took over the internet only towards the early 2000s, gaining momentum as the years swung by. Today, a strategically-placed Facebook or Instagram post can get you an immediate jump in the number of website visitors. Twitter, LinkedIn and Quora have helped boost online sales and create a stronger, clearer brand voice. Even YouTube has now launched a social feature where one can connect with friends and acquaintances on the video-streaming platform. Having a large social media following or being acknowledged by/getting a shout out from those with an army of followers is everything. However, the emphasis on creating engaging, shareable content that is a value-add to various users remains as strong as ever.
-
Mobile Search
In 2015, ComScore came out with a report that showed that the number of mobile-only users that had, had overtaken the number of desktop-only users. Mobile-first indexing is quickly changing how websites are crawled by Google, with plans of indexing all new websites this way in the near future. This means that web publishers and developers alike must pay attention to the mobile responsiveness of their website. This is only a recent development as there has been an unprecedented increase in the number of smartphone users in the past few years. In fact, those websites without proper mobile optimization might experience a decline in their position in SERPs (search engine results pages).
-
Going Local
If you own a business that serves people in one or more geographical locations, you will have to get your hands into a local search. Local search engine optimization is optimizing your website so as to increases the visibility of your business when your local customers or users are looking for it online. Local SEO can help users discover local businesses closest to them.
-
Knowledge Graph
New search features like Google’s Featured Snippet, Knowledge Graph, etc. have redefined the way information is discovered and used online. They have also given rise to more intense competition among websites to feature in the top spot on the SERP and grab the user’s attention. While SEO was all about focusing on the ranking of a webpage in the past, today, it is about so much more, including how users engage with a brand online. While SEO experts focused on spammy backlinks and keyword stuffing earlier, now, the onus lies on keyword intent, long-tail searches (specific multi-word keyword/search phrases) and quality backlinks founded on relationship building. The birth of the first blogs in the late 1990s is of great significance as popular bloggers have since helped spread the word about new-fangled online businesses of their liking, convincing legions of followers to visit their website with well-placed backlinks inside appealing content.
-
Machine Learning & AI
Machine Learning, a branch of Artificial Intelligence, has only recently emerged as a field of study. It uses data from past experiences or events to recognize patterns and perform various tasks without the need for explicit programming. Sundar Pichai, Google’s current CEO, has laid great emphasis on AI, stating that the search engine will be completely driven by it in the future. While many are opting for digital personal assistants like Alexa of Amazon or Apple’s Siri, chatting through chatbots, searching using images or even videos, the need for intelligent, contextual search is greater than ever before. And this can only happen with the integration of more and more AIML into Google’s core search algorithm.
The Future of SEO
In the past, a single, small search algorithm change would take long to implement, allowing many black-hat SEO techniques to help a webpage’s search rankings. Google is now vastly more vigilant and intelligent, constantly evolving to foster the steady growth of clean SEO tactics. Personalization is the name of the game, with users desiring more contextual, wholesome search results with the least effort from their side. Google might even use external platform data to accomplish this objective, something website owners can prepare for by optimizing in-app content to make it more user-friendly and tailored to suit user intent. Google will recognize patterns by accumulating data from different digital platforms and social media channels, making staying consistent across all of them with a single brand voice a wise move. Featuring well-optimized content, especially high-resolution images and videos, across all devices and in all forms (we are talking local search, mobile sites and voice search) is prudent. Reaching out to your customer base for valuable feedback on your online presence and communicating clearly with content creators must be your prerogative.
If you would like to know the current Google search algorithm updates, including the latest news about the Google IO 2019 conference, browse through the rest of our blog and keep coming back for even more on the constantly evolving world of search marketing.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
2.3 / 5. 3













6 thoughts on “A Brief History Of SEO & How SEO Has Evolved Over the Years”
Good post
Thank you, Subscribe to our blogs to stay updated with upcoming blogs.
Such a wonderful Article. It is very good to know the value of what we are working, How it came and this article really explained well about SEO. Thank you for sharing.
Thank you, Subscribe to our blogs to stay updated with upcoming blogs.
Great Post
We are glad that you liked our post. Check out our latest posts for more updates.