When scaling up your business one of the first things you do is update your website and its pages. In this stage, you can decide to merge various content.
You may further delete old content with information that is no longer relevant as you have created new content with updated information.
But what if the removed or merged content attracted a lot of traffic and is still at the top of the search results? In this case, you will need a code that redirects users to the new web page. This is when the 301 redirect comes into play.
There are many status codes that a browser sends to you when you might be searching for something on the Web. Common examples of these status codes are 404 – Not Found, 500 – Server Error, and 403 – Forbidden. 301 Redirects are one of these status codes, which act as a mail forwarder when you have permanently redirected the content of your Web page to another Web page.
What are 301 Redirects?
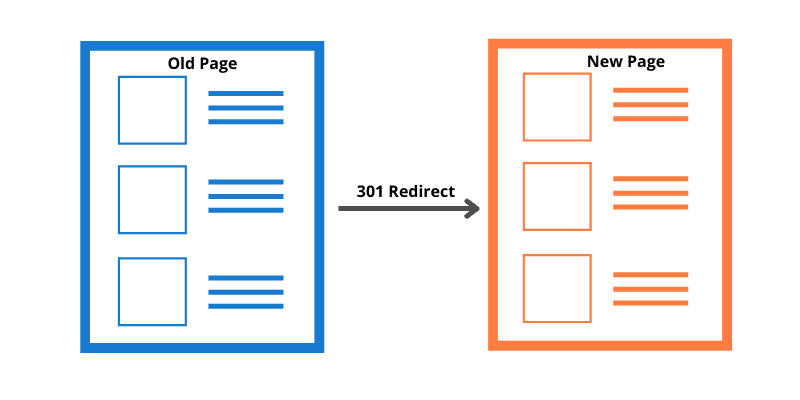
301 redirection is an HTTP status code that informs a browser when a web page has permanently moved to a new location. Crucially, if a user types in the older address, the 301 redirect automatically takes them to the new location.
Unlike a 301 redirect, a 302 redirect is for shifting a page’s location temporarily. Make sure you pick the right one as per your needs.

Unleash your website's potential by harnessing Infidigit's 400+ SEO audit to achieve peak site health & dominance on Google organic search.
Looking for an extensive
SEO Audit for your website?
Unleash your website's potential by harnessing Infidigit's 400+ SEO audit to achieve peak site health & dominance on Google organic search.

How Can 301 Redirects Boost SEO Performance?
Your SEO strategy can benefit significantly by using 301 redirects in various ways. They can eliminate the issues that restrict your website’s organic visibility. Moreover, 301 redirection for SEO is a means to thrive in the opportunities existing to drive growth.
You can boost your SEO performance by using 301s in the following ways:
1. Merge or Rewrite Thin Content Pages
Every website has pages that don’t perform as per expectations. They do not drive sufficient traffic or earn many backlinks. 301 redirects are result-driven ways to promote SEO performance as they contribute to content pruning. This involves merging pages with thin content to create meaningful pieces that describe a topic in detail.
Many Google algorithms, especially Panda, have emphasized the importance of quality over quantity. Therefore, an effective strategy for maintaining quality is SEO pruning, where underperforming pages are edited or cut off to build the strength of a website. Having little but impactful content is ideal.
2. Migrating the blog from a Subdomain to a Subfolder
One of the prominently used techniques to benefit from 301 redirects for quick SEO success is the migration of your blog from a subdomain to a subfolder. When you have in-depth content on your website, the algorithm views you as an authority and an expert on a specific topic. Generally, content earns a significant percentage of your site’s links.
When great links can improve your website’s SEO performance, it does not make sense to point them to a subdomain. You must include your blog in the site’s root unless technical restrictions do not allow you to do so. Migrate your company’s blog from a subdomain to a subfolder on priority.
3. Fixing Keyword Cannibalization Issues
For most SEO experts, keyword cannibalization is having two or more pages with the same target keyword, preventing either from ranking. However, the issue relates to intent. When the intent of more than one page is the same, you are competing with yourself, resulting in the issue of cannibalization.
301 redirects help in cleaning up problems and concerns arising from keyword cannibalization when there is no need to have all the competing pages.
4. Merge Multiple Websites into One
Migrating your company blog from a subdomain to a subfolder on your website helps boost SEO performance. Similarly, if you manage multiple websites for your business, merge all of them into one. When you combine the equity and authority of several domain properties, the result is a stronger website that drives more traffic and growth.
5. Managing Discontinued Products
There are two ways to manage discontinued products. For products that go out of stock due to discontinuation with poor chances of coming back, you must add a 301 redirect to the next best alternative. The strategy is more beneficial than deleting the page and displaying a 404 error to users who are trying to purchase an old product they come across. But, a redirect does not maintain the visibility or rankings of the discontinued product, passing on any equity to the target page.
The other alternative is to keep the pages for discontinued products, as users tend to have an interest in them even long after they are gone. A better solution would be to display alternatives for the discontinued products instead of removal or redirection from the original pages.
6. Publish the Revamped Page and Implement the 301 Redirect(s)
After you have identified underperforming pages, pages suffering from keyword cannibalization, and the multiple domains that require merging, it is time to implement changes and publish the pages. If any old URLs can do the job, you can republish the same URL. Then, you can delete the unnecessary pages/posts and add a 301 redirect to the new post.
How to resolve existing 301 redirect issues on your site?
If there are issues related to 301 redirects on your website, here’s what you can do to resolve them.
1. Ensure that the HTTP version of your site redirects to HTTPS
All websites must use HTTPS. It not only adds a layer of security but signals Google for ranking. Getting an SSL certificate has become easier than ever, and it is available for free. Therefore, there is no reason why a website should not use HTTPS.
However, it is insufficient to have an SSL certificate only. You must ensure that users are visiting the HTTPS version of the website, which requires a 301 redirect from the HTTP website to the HTTPS version.
2. Remove pages having 301 status codes from your sitemap.
To identify pages for crawling and indexing, Google assesses sitemaps. Pages with 301 status codes don’t technically exist, and getting Google to crawl them isn’t of any value. But the problem is that if such pages continue to exist in your sitemap, Google will visit them each time your website is crawled. This is unnecessary and results in the wastage of the crawl budget.
Open your sitemap URL. With the help of an online tool, download the URLs of all pages. Use a free HTTP status code checker to find all pages with 301 status codes. Remove these pages and replace them with the final redirect URL.
3. Fix redirect chains
When there are two or more redirects between the original and destination URL, it results in redirect chains. These chains are not beneficial in any way and only hinder user experience by slowing things down. Therefore, it is best to avoid them.
An online HTTP status code checker also allows you to inspect for redirect chains. Use it to find pages with two or more redirects. After you have identified the chains, you can either replace them with a single 301 redirect or replace internal links to redirect pages with direct links to the destination URL.
4. Fix redirect loops
If a URL redirects to another URL in the chain, a redirect loop occurs. This results in an infinite loop of redirects, which creates confusion and traps users as well as search engines. Find redirect loops with an online tool and then fix them in one of these two ways:
- Change the HTTP response code to 200 if the URL does not have to be redirected.
- Edit the final URL to eliminate the loop if the URL must redirect.
5. Fix broken redirects
Pages that redirect to a dead page are broken redirects. When visitors or search engine bots arrive at this page, they cannot view the final URL. Fix the error of broken redirects by restoring the dead page or deleting the links to the redirected URL.
6. Redirect 404 pages
A 404 status indicates that the page is dead. In some cases, it makes sense for the user to see the page. For instance, if the user enters the wrong URL, it will display an error message telling them that something is wrong. That being said, pages with 404 status codes require a resolution when they are still crawlable or have backlinks.
Find the problematic links and fix them by restoring the dead page, replacing or removing all internal links to the dead page, or using 301 redirects from the dead page to another relevant page.
7. Substitute 302 redirects and meta refresh redirects with 301s.
The 302 redirects are not appropriate for permanent redirects. They are for temporary moves. Meta refresh redirects are also not preferred by Google. Thus, if there are any 302 redirects or meta refresh redirects on your website, remove them at the earliest and replace them with 301 redirects.
8. Search for redirected (301) pages that get organic traffic
There shouldn’t be any organic traffic on pages with HTTP 301 status codes because they shouldn’t be in Google’s index. These pages can get traffic only if Google has not viewed the redirect.
If the 301 redirect on a page is recent, it isn’t too much of a problem. Google will crawl the page in its next turn, after which the page will be deindexed. To hasten the process, paste the URL into Google Search Console’s URL Inspection tool and then click on “Request indexing.”
Moreover, remember to remove these pages from the sitemap and submit it again via Google Search Console.
9. Search for “bad” external 301s
Many websites divert traffic to relevant third-party links and resources. This is good till the time the page it externally links to is not going elsewhere. If it does, it is irrelevant to the users and potentially even harmful. Make sure you check for bad external 301s and remove them.
Why opt for 301 redirection?
- If your business is moving to a new domain for rebranding purposes, 301 implementation is inevitable.
- HTTPS protocol is the order of the day, and if you’re migrating from HTTP then a 301 redirect is crucial to avoid the dreaded ‘404-Not Found’ code.
- If you’re looking to overhaul your content is another reason why 301 redirection might be the way to go.
Is 301 redirection SEO friendly?
Absolutely! However, you need to implement 301 redirection while keeping search engine rankings in mind. The keywords used in your new URL and content should be in accordance with your industry so that your overall rankings are not adversely affected by your latest 301 move.
How does a 301 redirect work?
1. Client requests a URL from a server
As a primary step towards understanding how a 301 redirect works, you need to understand what happens when a client first requests an URL. The client requesting for an URL opens the server connection and sends it through. The instance below might give a broader view of the event.
“GET /old-url/ HTTP/2”
Main Host: www.infidigit.com
2. Server response
After the client requests the URL, in 301 redirection SEO, the server immediately begins to treasure it. Instantly after, the server tries understanding and looking up the URL of 301 redirect. It then reciprocates that the content the user is searching for has permanently relocated and responds with,
HTTP/2 301
Location: https://www.infidigit.com/new-url/
3. Client makes a new request
After being informed about the relocation, the client then requests the new location of the content. The usual response is as in the instance given here,
GET /new-url/ HTTP/2
Main Host: www.infidigit.com
4. Server responds to new request
Assessing the request, the server evaluates the new request about the 301 redirects. After understanding the demand, the server responds by approving the request and further reciprocates the new URL asset, alongside the payload. It often shows as like, HTTP/2 200
When to Implement 301 Redirection?
-
When moving a page to a new URL permanently
There are many instances when you might need to shift the content on a page to a new URL. For instance, if there was SEO-related content on “https://www.website.com/old_page/” which was moved to “https://www.website.com/new_page/” then a 301 redirection must be used for this permanent redirect. This will help the users to get redirected to the new page and the search engine to index the new page and keep its ranking intact.
-
Site migrating to a new domain
Businesses change their domain names for many reasons, such as expanding the reach of their website overseas, rebranding, and so on. A few examples of website migration include:
- Changing the name of the website from https://www.oldwebsite.com to https://www.newwebsite.com
- Changing the domain name from https://website.com to https://www.website.co.uk
Using the “change of address” tool from the Search Console of Google, a 301 redirection should be implemented in such cases.
-
Moving from HTTP to HTTPS
HTTP and HTTPS protocols play a crucial role in the indexing process of search engines. Many websites have shifted to the HTTPS protocol, while some still use the HTTP protocol. Hence, if you’re switching from HTTP to HTTPS, it is imperative that you use 301 redirects as they help the search engines index your protocol shift. They prevent the “404 – Not Found” code from showing up and redirect the user to the new page.
-
Moving from non-www to www URL
This is primarily to avoid any duplication issues. https://website.com and https://www.website.com are the two options here.
If you observe that your website is accessible through both non-www and www URLs, then it is important to implement 301 redirects to your preferred URL. Since there are no SEO benefits of choosing either URL structure, you can choose either of these for your website based on your preference.
-
Resolving uppercase and trailing slash
Trailing slashes are an important part of the URL structure. A URL with a trailing slash will be different from a URL without a trailing slash. For instance, the URL https://abc.com/page will redirect to a different page than the one https://abc.com/page/ redirects to. Hence, it is important to maintain consistency in using trailing slashes for your URLs. Apply 301 redirects to the version of the URL that you do not intend to use.
The use of Upper Cases can cause similar problems too. https://abc.com/page/ will be a different Web page than the one associated with https://abc.com/Page/.
-
Recreating Content
Many businesses might want to entirely rebuild their old content, maybe on a new page, due to multiple reasons. In cases like these, you should ensure that a 301 redirect guides users from the old content to the new one. While many forget to unpublish the old site, it is obligatory to archive it so that users can effortlessly find the new content page.
Usually, when attempting 301 redirects, it is better to devise a flexible rule. If it is unavailable, use a particular tool for the same reason, alongside Google sheets or Excel especially to have a basic roadmap of your redirects.
301 Redirect vs. a 302 Redirect
A 301 redirect notifies search engines as well as users that the page has permanently shifted, while simultaneously taking them to the accurate page. Thus, users are redirected to the new page that has substituted the old one.
Meanwhile, if you decide to relocate the existing content to a new URL only for a temporary time period for reasons like website testing and want to guide users to a short-term URL, then you can use 302 redirects.
301 vs. 302 vs. 307 Redirects
302 redirects are also common, but they differ in that a 302 redirect indicates a temporary move, while a 301 redirect indicates a permanent move.
The most common uses of 302 redirects are for getting customer feedback or testing changes. Once this is done, the page is expected to come back.
The purpose of using a 307 redirect is also to indicate temporary moves. 302 redirects distinguish themselves from 307 redirects in a way that the HTTP method does not change in a 307 redirect. The HTTP method can alter with a 302 redirect.
SEO experts must use a 301 redirect if the URL has moved permanently from its initial location to its destination.
302 vs. 307 redirects: Which Redirect Should I Use?
Both 302 and 307 redirects are used for temporary moves. The content, too, will return soon. Since it is evident how search engines react to 302 redirects, it is advisable to use that instead of the 307 redirects.
There is only one significant difference between the 302 redirects and 307 redirects. When using a 307 redirect, the HTTP method does not change. For example, if the URL uses the GET HTTP method, the redirect will also use the GET HTTP method. Moreover, the 307 redirects are used as internal redirects when HTTPS is enforced.
Difference between a 301 redirection in SEO and the rel=” canonical” attribute
A 301 redirection comes into the picture when you have permanently moved any page or wish to transfer any gained SEO credit to the different web pages. It also holds importance when you want to deindex any page. In simple terms, 301 redirection in SEO informs Google about the preceding things.
On the other hand, rel=canonical informs search engines that information on identical URLs is the same. It is critical since this approach allows you to instruct search engines on which pages to display to users. Some cases where rel=canonical usage is necessary are
- When you can’t implement 301
- In case you wish to retain numerous pages with identical content active.
How to redirect a page using WordPress?
-
Redirect via server
This is one of the most effective methods, both from the perspective of page loading speed and technical efficiency. WordPress doesn’t enable 301 redirects directly. Hence, redirection using the server is the most preferred option. Although this approach totally depends upon the stack of software your WordPress domain might be using.
-
Redirect using plugins
You should only go for this option if, for some reason, redirecting via a server is not working out for your domain. Using plugins for 301 redirects will be comparatively slower and will rely heavily on a third-party, which might not be very trustworthy.
How to Redirect a Page Using Shopify?
This is how you can redirect a page using Shopify:
- Go to “Online Store” and then select “Navigation” on the menu
- Click “URL Redirects” below the page’s header
- Click “Create URL Redirect”
- Now paste the original URL and then the new URL
- Save the redirect
How to Redirect a Page Using BigCommerce?
Here’s how 301 redirection SEO can be done using BigCommerce:
- Go to “Settings” and then select “301 redirects.”
- Click “Add Redirect”.
- Type the page URL preceded by a / under the “Old URL” field and “Save” the changes.
- In case of redirection from a reserved URL, you will be warned of the potential risks. Click “Ok” to proceed or “Cancel” to cancel the redirect.
- Now select the “Redirect Type” that consists of manual and dynamic redirects.
Few Mistakes to Avoid in 301 Redirections
Once you know what 301 redirect is, here’s how to avoid 301 redirection SEO:
-
Allowing Pages to 404
A 404 occurs when you delete a page from the website and the server, but links to the page still exist. It is a “Page Not Found.” Allowing too many pages to 404 can disrupt user flow and affect your SEO. So, make sure that all 404s are 301s redirected to a relevant page.
-
Using Redirects Rather Than Updating Broken Internal Links
Instead of redirecting your internal links that result in 404 to the homepage, make sure you update the links with the closest contextual links having significant value.
-
Redirect Chains & Loops
Redirect chains are formed when more than one redirect leads to the final page. A redirect loop, however, is when a URL redirects to itself, due to which the page never loads. These two mistakes in 301 redirections SEO can make it challenging to navigate your website, hamper your SEO efforts, and impact your leads and conversions.
Few mistakes to avoid in 301 redirection
-
Setting 302 redirection
301 redirects are used for permanent redirection of a Web page, and 302 redirects are used for temporary redirection of a Web page. It is common to confuse them both. Use the Site Audit Tool to identify which redirection status is used on your Web page.
-
Redirecting a page where the intent differs from the original one
Proper organization and record-keeping can help you avoid this mistake. Make sure that the users are redirected to the page they’re looking for and not another Web page.
-
Javascript redirection
Javascript redirection should be avoided at all costs as there is a high possibility that search engines won’t be able to render the page. Many websites do not allow JS or CSS files to be crawled, which can cause this issue.
-
301 redirects after creating a new page
When you create a new page or, for some reason, permanently move the content of your existing page to a new one, you can use the 301 redirect status code to inform users about the redirection and lead them to your current page through a redirection link or button.
-
302 redirect during the content migration
When you migrate or move your existing content to a new page or URL for a temporary duration in case you are testing your page, assessing its performance, gathering client feedback or fixing any other issue, and want users to know about the migration, you can use a 302 redirect.
Other Types of Redirects
-
302 – Temporarily Moved
When you temporarily move the address of your Web page (URL) from one page to another, you can inform existing and prospective users about the page shift through a 302 response status code. This code redirects customers from the old page to the new one and also notifies search engines about the temporary shifting of pages.
-
Meta Refresh or JavaScript Redirect
A Meta Refresh or JavaScript Redirect helps redirect users to your new Web page or URL. But unlike a 302 response status code where users have to click the redirection link to go to the new page, the Meta Refresh or JavaScript Redirect enables the Web browser to automatically redirect itself to the new page after a short time frame.
-
Internal 404 Errors
An Internal 404 Error appears when a website’s content has either been deleted or shifted to a new website or URL altogether. When a Web owner fails to make adjustments to the website’s internal links due to an incorrect entry of the change, users trying to reach the website can see a 404 Error Not Found status code on their browsers. It also happens if the Web server or domain name does not exist anymore or if the user’s connection is broken. Here, the user is neither t automatically redirected nor provided any link for redirection. However, to fix 404 errors, you need to carry out a 301 redirect as a Web owner if you have moved your website permanently or a 302 redirect if you have moved it temporarily. As a user, you can fix 404 errors by refreshing the page or re-entering the URL in the search engine box again.
How Do 301 Redirects Affect SEO?
It is crucial to know when and how to implement a 301 redirect, or else it can affect your Search Engine Optimization (SEO) rankings on Web browsers (mostly Google). SEO rankings affect the position of the website’s display when a user uses the browser to search for a product or service. These rankings depend on keywords in your Web content and URL and match the user’s keyword.
When you use specific keywords in your content and URL, it gathers traffic as per the SEO rankings achieved. Moving your Web page to a new one with a 301 redirect that consists of keywords unrelated to your existing content or URL harm SEO rankings and makes it difficult for users to visit your new website. To maintain SEO rankings, it is best to use as many of the target keywords that were used to drive traffic to your old Web page to ensure that you do not lose out on existing or prospective customers.
Conclusion
Infidigit is an SEO company in Mumbai that offers professional SEO services that can help you with the technical aspects of SEO, like 301 redirects. With competent SEO experts, our team offers an error-free and expansive range of SEO-related services that can help your business generate optimum traffic and revenue.
Popular Searches
How useful was this post?
0 / 5. 0